DMLS and EBM are both powder bed fusion 3D printing technologies. Their difference lies in how they melt the metal powder to create a final part. DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) makes use of a fiber laser whereas EBM makes use of an electron particle beam. EBM (Electron Beam Melting) produces highly dense parts but suffers from a poor surface finish. DMLS also produces highly dense parts but has an improved surface finish.
This article will compare DMLS vs. EBM in terms of their differences, materials, and printing technology.
DMLS Definition and Comparison to EBM
DMLS is a powder bed fusion 3D printing technology used to manufacture metal parts. EOS first commercialized the technology in 1995 and is the owner of the DMLS trademark. DMLS works by selectively melting a metal or metal alloy powder with a high-powered laser beam, which is typically referred to as a fiber laser. The laser beam traces out the cross-section of a part layer. It then melts the metal particles together. The print bed then moves down and another layer of metal powder is applied. Inert gas occupies the build chamber to prevent oxidation during printing. EBM printers also need an oxidation-free environment, but they achieve this with a vacuum chamber instead.
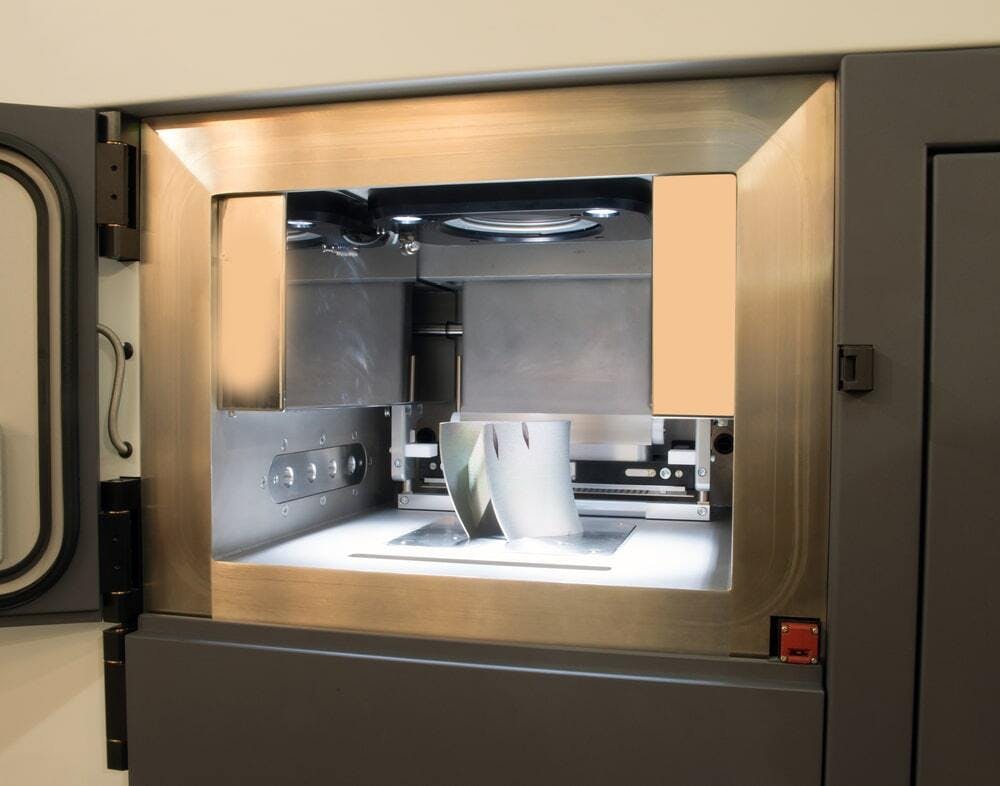
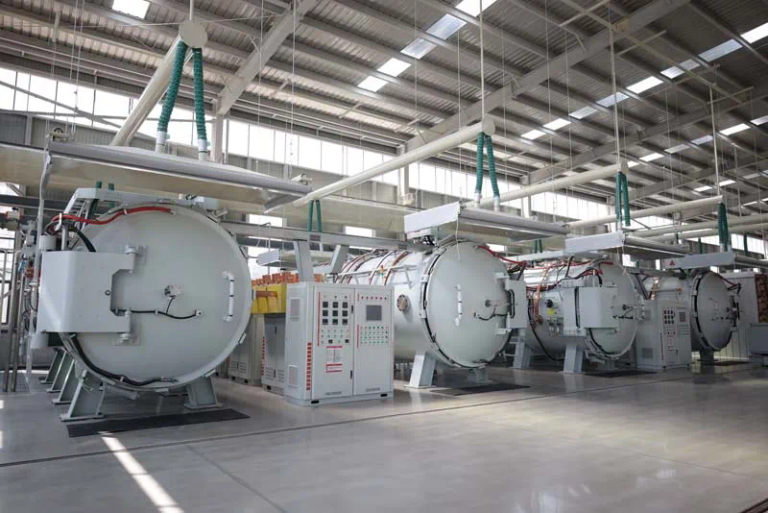
The image below shows a DMLS machine:
A DMLS machine.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/Moreno Soppelsa
What Are the Advantages of DMLS Compared to EBM?
The key advantages of DMLS vs. EBM are:
- DMLS can print parts with higher resolution. This is because a DMLS laser beam is narrower than an electron beam.
- DMLS offers far more materials than EBM and is, therefore, more versatile.
What Are the Disadvantages of DMLS Compared to EBM?
Some key disadvantages of DMLS vs. EBM include:
- DMLS parts can have internal stresses when compared to EBM parts. The high-temperature environment in an EBM can help relieve stress in a part.
- DMLS cannot print parts with extremely high melting temperatures.
EBM Definition and Comparison to DMLS
EBM is a powder bed fusion 3D printing technology used to manufacture metal parts. Arcam first developed the technology in 1993 in collaboration with Chalmers University of Technology. In 2016, GE (General Electric) purchased controlling shares in Arcam.
EBM works by selectively melting a metal or metal alloy powder with a high-energy electron particle beam. That is, instead of energized photons like those in a laser, EBM makes use of energized electrons. The electron beam traces out the cross-section of a part layer and melts the metal particles together. After each layer is formed, the print bed moves down and another layer of metal powder is applied. EBM must take place within a vacuum to prevent oxidation due to the extremely high temperatures generated by EBM.
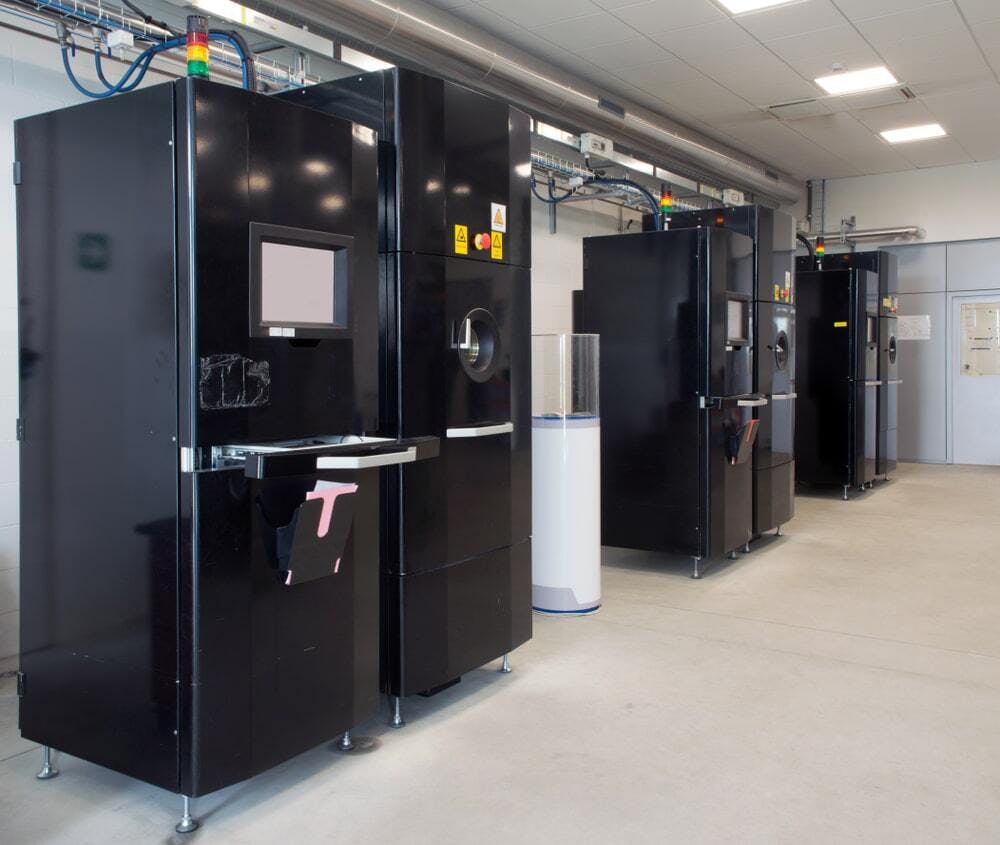
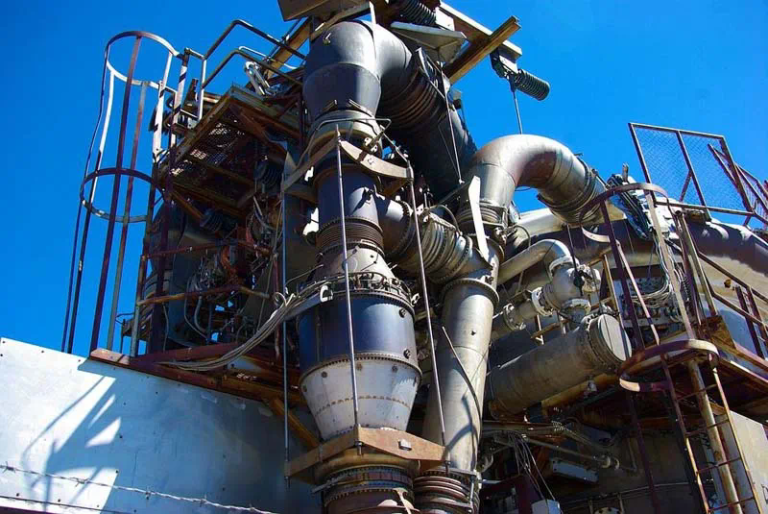
A typical EBM machine is shown in the image below:
An EBM machine.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/Moreno Soppelsa
What Are the Advantages of EBM Compared to DMLS?
Some key advantages of EBM vs. DMLS are:
- EBM can melt very high-temperature materials and can reach temperatures of 2,000°C.
- Despite having only one beam, EBM can direct the beam at an extremely high speed, effectively mimicking the functionality of multiple beams.
What Are the Disadvantages of EBM Compared to DMLS?
Some key disadvantages of EBM vs. DMLS include:
- EBM needs to print inside a vacuum chamber. This adds cost and complexity to the system.
- EBM can only use conductive metals. As such, it has a limited range of potential materials.
Comparison Table Between DMLS and EBM
The table below lists some of the more common properties of DMLS vs. EBM as well as how they compare with each other:
Number of beams
4
1 – Very quick beam positioning
Beam power
400 W
4500 W
Requires vacuum build volume
No
Yes
Layer height
30 to 40 microns
70 microns
Has isotropic material properties
Yes
Yes
Parts need to be cooled after printing
Yes
Yes – often overnight
Parts need support structures
Yes
Yes
Largest print volume
400 x 400 x 400 mm
350 OD x 430 H (cylinder)
Table: DMLS vs. EBM Comparison
DMLS vs. EBM: Technology Comparison
Both DMLS and EBM are powder bed fusion technologies that use an energy source to melt a metal powder layer by layer to produce a final part. However, EBM makes use of an electron beam as the heat source whereas DMLS makes use of a fiber laser beam.
DMLS vs. EBM: Material Comparison
DMLS is able to use many more materials than EBM. EBM can typically only make use of titanium alloys, cobalt/nickel alloys, and pure copper.
DMLS vs. EBM: Product Applications Comparison
DMLS is heavily used in the medical industry for dental devices or for implants like hip joints. EBM is used in aerospace, medical, military, and R&D environments to produce advanced components.
DMLS vs. EBM: Print Volume Comparison
Print volume size is comparable with these two technologies. The DMLS build volume must be filled with an inert gas like argon, whereas an EBM machine must create a vacuum in which to print.
DMLS vs. EBM: Surface Finish Comparison
DMLS has a better surface finish than EBM. This is because the electron beam is wider than the DMLS beam, and this creates a more visible surface roughness on EBM parts.
DMLS vs. EBM: Cost Comparison
EBM is significantly more complex when compared to DMLS. This is because EBM generates a stream of electrons and maintains a vacuum build chamber. However, pricing is comparable between the two. An entry-level DMLS machine costs anywhere from around $350,000, whereas an entry-level EBM machine can cost upwards of $250,000. It must be noted that metal powders also add to the cost as they can cost upwards of $300 per kg.
What Are the Mutual Alternatives to DMLS and EBM?
Despite the benefits of DMLS and EBM, below is an alternative technology that can achieve similar results:
- SLM: Selective laser melting is a powder bed fusion technology owned by SLM solutions. SLM uses a high-powered laser beam to melt a metal powder. It can make use of up to 12 lasers to print multiple parts simultaneously. SLM also needs to print in an inert gas environment like DMLS. SLM has higher laser energies when compared to DMLS but still does not approach EBM’s beam energies. See our full comparison guide on DMLS vs. SLM.
What Are the Similarities Between DMLS and EBM?
Some of the similarities between DMLS vs. EBM are:
- Both EBM and DMLS are powder bed fusion metal printing technologies that make use of a heat source to melt a metal powder.
- Both technologies are used for parts in the medical industry.
What Are the Other Comparisons for DMLS Besides EBM?
Aside from EBM, the following is an alternative technology to DMLS:
- DMLS vs. Binder Metal Jetting: Binder Metal Jetting technology makes use of a metal powder that is bound together with a polymer binder. The binder is applied to take the shape of the part cross-section. Another layer is then added on top and the process repeats. When the part is complete, it must be post-processed to sinter/fuse the metal powder together while burning off the binder.
What Are the Other Comparisons for EBM Besides DMLS?
Aside from DMLS, the following is an alternative technology to EBM:
- EBM vs. DED: DED (Directed-energy deposition) is a metal printing technology that feeds a metal wire to a printing nozzle. The metal is then melted at the nozzle and deposited on the build plate layer by layer, similar to FDM printing. This produces parts that have homogenous mechanical properties, similar to those made with EBM printers.
Summary
This article summarized the differences between DMLS and EBM 3D printing technologies.
To learn more about DMLS vs. EBM and to help select the perfect technology for your products, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry offers a full range of 3D printing services for your project needs. Visit our Instant Quote Engine to get a free, no-obligation quote in minutes.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.

.webp)