The Horizontal Graphite Condenser: Design and Benefits
The Horizontal Graphite Condenser (HGC) has emerged as a pivotal component in various industrial processes, graphite condensation reaction particularly in the field of heat exchange technology. This condenser type leverages the unique properties of graphite, providing efficiency and reliability that traditional materials often fail to achieve. This article delves into the intricate design aspects of HGCs, their operational principles, and the myriad benefits they offer across different applications.
h2: Overview of Horizontal Graphite Condensers
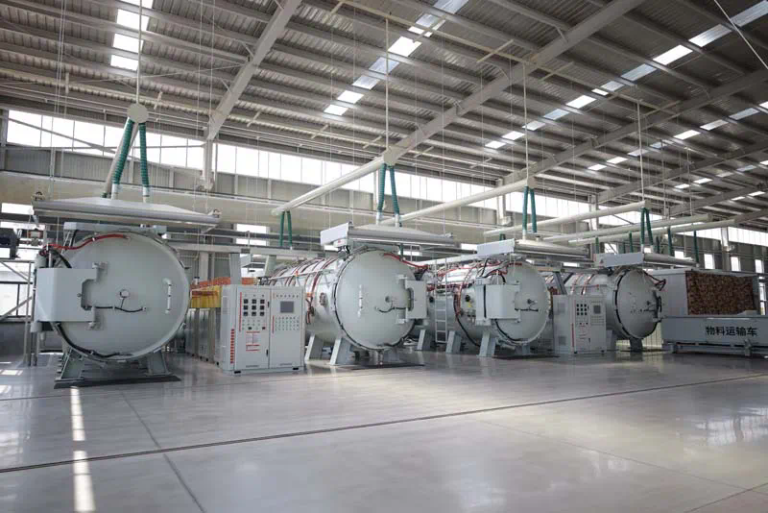
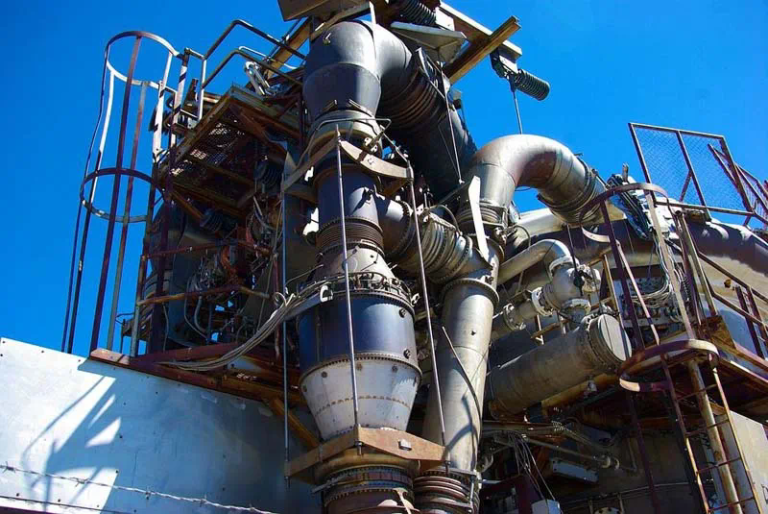
Horizontal Graphite Condensers are specifically designed to facilitate the condensation of vapor into liquid by transferring heat from the vapor to a cooling medium. The horizontal orientation allows for efficient drainage of condensed liquids, minimizing the chances of flooding in the system.
Graphite, known for its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, is the material of choice for these condensers. Its unique properties enable HGCs to operate effectively in aggressive environments where traditional metallic condensers might suffer from rapid degradation.
h3: Key Design Features

1. Material Selection
The selection of graphite as a primary material is crucial. Graphite’s high thermal conductivity ensures that heat transfer occurs efficiently, while its resistance to chemical attack makes it ideal for use in corrosive environments. Additionally, graphite’s low density allows for lightweight designs without compromising structural integrity.
2. Configuration and Orientation
The horizontal configuration of HGCs facilitates optimal flow patterns and enhances the gravitational drainage of condensate. This design not only improves heat transfer rates but also helps maintain a stable operation by preventing vapor accumulation within the condenser.
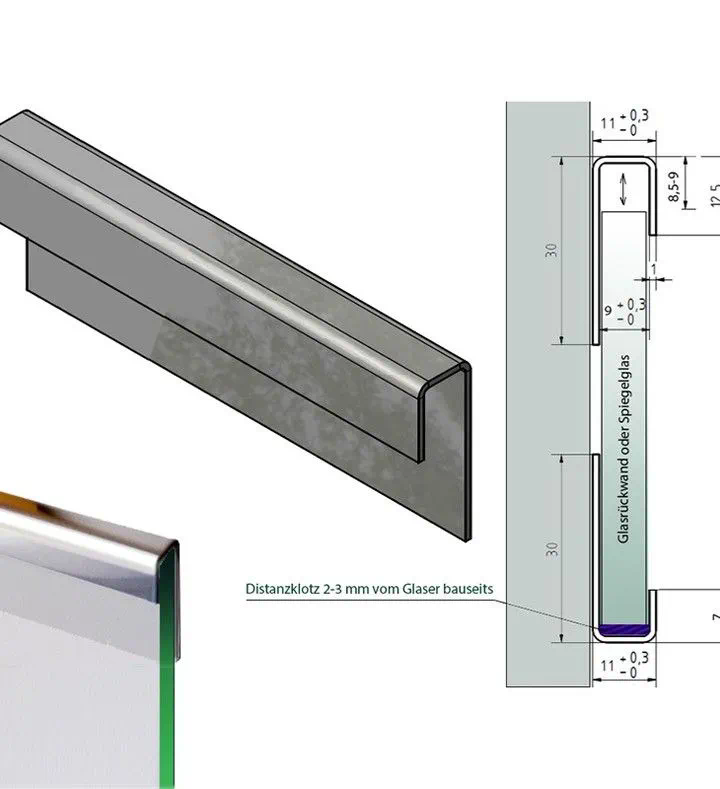
3. Heat Transfer Surfaces
The design includes extensive heat transfer surfaces, which can be customized based on application requirements. These surfaces can be optimized for varying flow conditions, ensuring that the condenser operates at peak efficiency.
4. Cooling Medium Integration
Efficient integration of the cooling medium is vital. HGCs can utilize different cooling fluids, including water and air, depending on the specific needs of the application. This flexibility allows industries to tailor their systems for maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
h2: Operational Mechanism
The operational mechanism of a Horizontal Graphite Condenser revolves around the principles of heat exchange. Vapor enters the condenser and comes into contact with the cooler graphite surfaces. As the vapor releases its latent heat, it undergoes a phase change into a liquid state.
The horizontal design ensures that this process occurs smoothly, allowing the liquid to drain away from the heat exchange surface due to gravity. This arrangement minimizes the risk of vapor trapping, which can lead to inefficiencies and potential damage to the condenser.
h3: Advantages of Horizontal Graphite Condensers
1. Enhanced Thermal Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of HGCs is their enhanced thermal efficiency. The combination of graphite’s superior thermal conductivity and the horizontal design maximizes heat transfer rates, leading to reduced energy consumption.
2. Corrosion Resistance
In industries dealing with aggressive chemicals, the corrosion resistance of graphite offers a substantial advantage over traditional metallic condensers. This durability results in longer operational lifetimes and reduced maintenance costs.
3. Reduced Footprint
The horizontal configuration allows for compact designs, making HGCs suitable for locations with space constraints. This reduction in footprint can lead to lower installation costs and greater flexibility in system design.
4. Versatility Across Applications
HGCs find applications in various sectors, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, power generation, and food processing. Their ability to handle a wide range of operating conditions makes them a versatile choice for many industrial needs.
h2: Applications of Horizontal Graphite Condensers
The versatility of Horizontal Graphite Condensers enables their application in numerous industries, each benefiting from the unique properties of graphite.
h3: Chemical Processing
In the chemical industry, HGCs are employed for processes involving volatile organic compounds and other corrosive substances. Their resistance to chemical attack ensures reliable performance, while their thermal efficiency aids in maintaining optimal reaction temperatures.
h3: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical production often requires precise temperature control and the handling of sensitive compounds. HGCs provide a stable platform for condensation processes, ensuring that active ingredients are preserved without degradation.
h3: Power Generation
In power plants, particularly those utilizing steam cycles, the efficient condensation of exhaust steam is critical. HGCs enable rapid heat removal, improving the overall efficiency of the power generation cycle and reducing emissions.
h3: Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage sector, temperature control is paramount for preserving product quality. HGCs facilitate the condensation of vapors generated during processing, ensuring that products remain safe and flavorful.
h2: Challenges and Considerations
While Horizontal Graphite Condensers offer numerous advantages, there are also challenges that must be addressed to ensure successful implementation.
h3: Initial Costs
The initial investment for HGCs can be higher than that for traditional condensers. However, the long-term savings in maintenance and operational costs often offset this initial expenditure.
h3: Installation Requirements
Proper installation is crucial for maximizing the benefits of HGCs. Careful consideration of orientation, support structures, and integration with existing systems is necessary to achieve optimal performance.
h3: Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is essential to keep HGCs operating efficiently. Although graphite is durable, it is still important to monitor for any signs of wear or damage, particularly in harsh operating conditions.
h2: Future Trends in Horizontal Graphite Condenser Technology
The future of Horizontal Graphite Condenser technology looks promising, driven by advancements in materials science and engineering processes.
h3: Advanced Coatings
Research into advanced coatings may enhance the performance of graphite condensers further. These coatings could provide additional protection against wear and improve thermal efficiency.
h3: Smart Monitoring Systems
The integration of smart monitoring systems will allow for real-time performance tracking of HGCs. By utilizing sensors and data analytics, operators can optimize performance and preemptively address maintenance needs.
h3: Sustainability Initiatives
As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, HGCs will play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption and emissions. Their efficient operation aligns well with global initiatives aimed at minimizing environmental impact.
In conclusion, Horizontal Graphite Condensers represent a significant advancement in heat exchange technology. Their innovative design and inherent benefits make them an excellent choice for a diverse array of applications. As industries continue to evolve and demand greater efficiency, HGCs are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of thermal management solutions.